Introduction
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, websites and applications must be fast, scalable, and flexible. Traditional content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal have long dominated the market, but the growing demand for omnichannel experiences has given rise to a new approach—Headless CMS.
In this article, we’ll explore what a Headless CMS is, how it differs from traditional CMS, its advantages, disadvantages, real-world use cases, and why developers and businesses are increasingly embracing this modern architecture.
What is a Headless CMS?
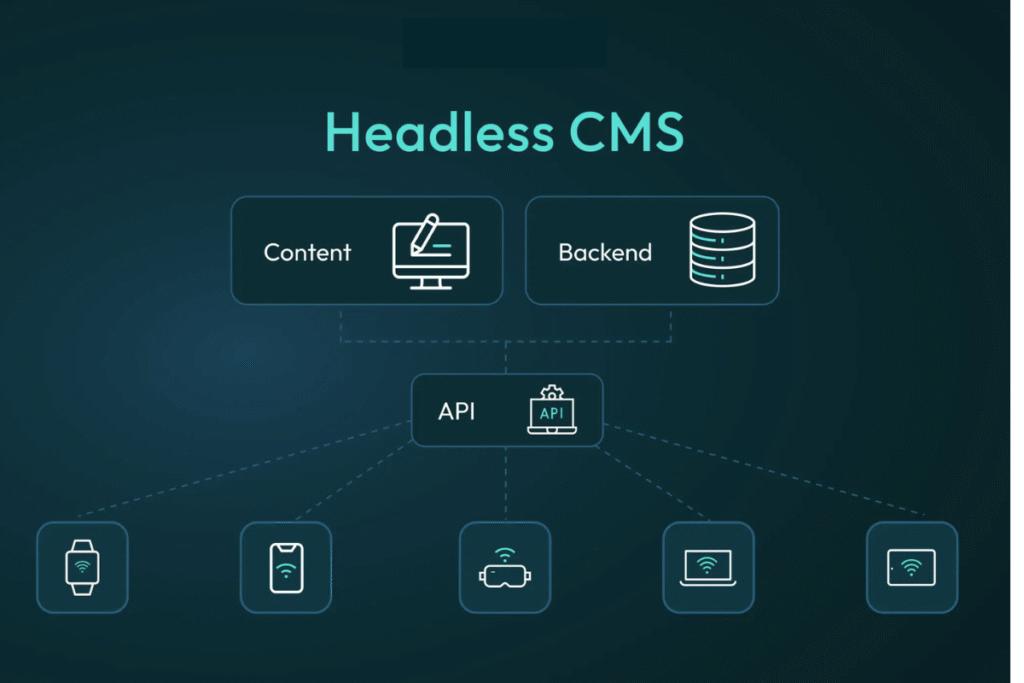
A Headless CMS is a content management system that separates the backend (content repository) from the frontend (presentation layer). Unlike traditional CMS platforms, where content and design are tightly coupled, a headless CMS delivers content through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), leaving developers free to design and present that content using any technology.
In simple terms, the “head” (frontend) is removed, and the CMS focuses only on storing, organizing, and delivering content. Developers then use frameworks, libraries, or frontend technologies like React, Angular, Vue.js, or even mobile applications to display this content.
Traditional CMS vs. Headless CMS
1. Traditional CMS
-
Tightly coupled: Backend and frontend are linked.
-
Examples: WordPress, Joomla, Drupal.
-
Content delivery: Designed for websites only.
-
Limitations: Difficult to deliver content across multiple devices like mobile apps, IoT devices, and smart TVs.
2. Headless CMS
-
Decoupled architecture: Backend and frontend are separate.
-
Examples: Contentful, Strapi, Sanity, Prismic.
-
Content delivery: Delivered via APIs, accessible by multiple platforms.
-
Advantages: Flexibility, scalability, and better developer control.
How Does a Headless CMS Work?
The workflow of a headless CMS can be summarized in three main steps:
-
Content Creation
Editors create and manage content using the CMS backend dashboard. The system stores this content in a repository. -
Content Delivery
Instead of binding content to themes or templates, the CMS exposes it through APIs (RESTful or GraphQL). -
Content Presentation
Developers fetch the content and present it across multiple platforms—websites, mobile apps, smart devices, digital kiosks, or even AR/VR environments.
This separation provides unmatched freedom in terms of content reuse and platform compatibility.
Benefits of Using a Headless CMS
1. Omnichannel Content Delivery
Headless CMS allows businesses to deliver content seamlessly to websites, mobile apps, IoT devices, smartwatches, and other digital touchpoints.
2. Faster Performance
Since frontend technologies like React, Vue.js, or Next.js can be used, websites load faster, offering users a smoother experience.
3. Scalability
APIs make scaling easy. Adding a new channel doesn’t require redesigning the whole CMS.
4. Developer Flexibility
Developers can choose any programming language or frontend framework. This flexibility fosters innovation and efficiency.
5. Content Reusability
The same content can be reused across different platforms, reducing redundancy and effort.
6. Future-Proof
As new devices and platforms emerge, businesses can quickly integrate them without replacing their CMS.
Challenges and Limitations of Headless CMS
While headless CMS offers numerous advantages, it also comes with certain drawbacks:
-
Complex Setup: Requires more technical knowledge compared to traditional CMS.
-
No Built-in Frontend: Businesses need developers to design and implement the presentation layer.
-
Higher Initial Cost: Setup and maintenance can be costlier.
-
Learning Curve: Editors and marketers may find it less intuitive without traditional preview options.
Popular Headless CMS Platforms
-
Contentful – Cloud-based, API-first, widely used by enterprises.
-
Strapi – Open-source, Node.js-based, highly customizable.
-
Sanity – Real-time collaboration, flexible data modeling.
-
Prismic – Offers a user-friendly interface with strong API support.
-
GraphCMS (Hygraph) – Strong GraphQL-first CMS.
Use Cases of Headless CMS
-
E-commerce
Businesses can deliver product details across websites, apps, and marketplaces seamlessly. -
Media and Publishing
Deliver content to websites, apps, smart TVs, and podcasts from a single repository. -
Corporate Websites
Enterprises use headless CMS for better scalability and integration with multiple services. -
IoT Applications
Headless CMS provides content to wearables, digital assistants, and connected devices. -
Multilingual Websites
With centralized content management, it becomes easier to handle multiple languages and regions.
Headless CMS vs. Decoupled CMS
-
Decoupled CMS: Backend and frontend are separate but still connected with a predefined presentation layer.
-
Headless CMS: Backend is completely independent, giving developers total control over the frontend.
While both offer flexibility, headless CMS is more advanced for multi-platform content delivery.
Future of Headless CMS in Web Development
As user behavior shifts toward multi-device engagement, headless CMS adoption will continue to rise. With advancements in Jamstack architecture, serverless technologies, and AI-driven personalization, headless CMS will play a central role in web development.
Businesses seeking to future-proof their digital presence will increasingly move from traditional CMS to headless CMS solutions.
FAQs
What is the main difference between a traditional CMS and a headless CMS?
A traditional CMS combines content management and presentation, while a headless CMS separates them, delivering content via APIs.
Do I need coding skills to use a headless CMS?
Yes, developers are usually required to set up the frontend since headless CMS doesn’t provide built-in themes or templates.
Can a headless CMS be integrated with WordPress?
Yes, WordPress can be used in a headless mode where it serves as the backend while frontend frameworks like React or Next.js handle presentation.
Is a headless CMS suitable for small businesses?
It depends. Small businesses with limited digital presence might prefer traditional CMS, but those planning omnichannel experiences can benefit from headless CMS.
Which industries benefit most from headless CMS?
E-commerce, media, publishing, and enterprises with multi-device strategies benefit the most.
Conclusion
Headless CMS represents a paradigm shift in web development, offering flexibility, scalability, and omnichannel content delivery. While it may require more technical expertise and higher initial investment, the long-term benefits—such as faster performance, content reusability, and future-proofing—make it an attractive option for modern businesses.
As digital transformation accelerates, adopting a headless CMS may well be the key to staying competitive in today’s multi-device, content-driven world.